
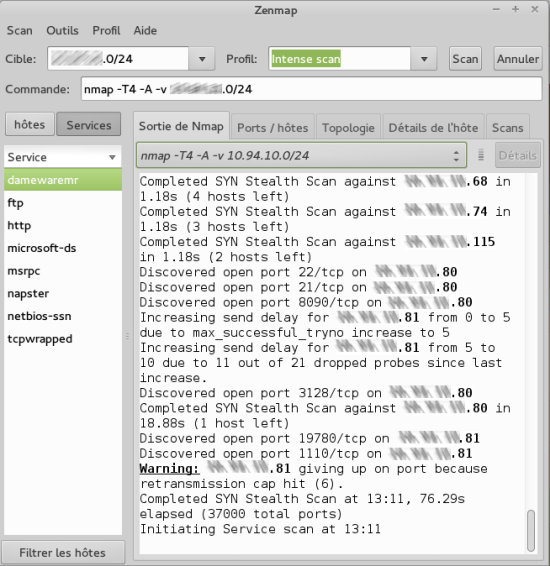
MAC Address: 88:DD:EA:DD:CE:37 (Texas Instruments) MAC Address: 50:C7:FF:FF:15:FF (Tp-link Technologies) The output of the above command produces something like: # nmap -sn 192.168.0.0/24 If we want to run a quick scan of machines in our network without trying to see if any port is open, we run: # nmap -sn 192.168.0.0/24 Multiple networks can be scanned at once. MAC Address: 50:ff:BF:ff:ff:AC (Tp-link Technologies) Nmap scan report for Archer.lan (192.168.0.1) Running a scan without any argument except the network address yields the following: # nmap 192.168.0.0/24 Let's assume your local network is 192.168.0.0/24, and you want to run a scan on this network. You also should consult the Nmap man page by running man nmap.
After installing Nmap, you can run the nmap command without arguments to display all of its options. Substitute dnf for yum if you are on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 or newer. To install Nmap on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 or Fedora, you'd run: # dnf -y install nmap
#ZENMAP FOR KALI HOW TO#
In the following post, we'll walk you through on how to install Nmap, use it, and, most important, get more to know about your network. Cheat sheet: Old Linux commands and their modern replacementsīesides being free, Nmap is very flexible, portable, well-documented, and easy to use.Linux system administration skills assessment.A guide to installing applications on Linux.Download RHEL 9 at no charge through the Red Hat Developer program.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
